2D points 3D Objects 3D Points Boundary Cursor position Data for selected object Domain Expansion Field Field components Field formula Field tubes Function Generate expansions along 2D boundary Generate expansions for 3D objects Grid formula Grid transformation Info and movie directives Insert Integral Modify 2D expansions MMP Movie Open GL window PET basis PFD (predefined FD) Project Space, plane, arrow, or point Tools and draw Transformation data Window
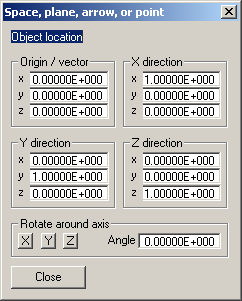
This dialog is opened when you press a button in another dialog that requires 3D data input for defining a 3D point, arrow (point+direction), plane (point+2 directions), or space (point+3 directions).

A space in OpenMaXwell, is defined by four vectors. One vector defines the location of the origin and the other three define the three directions of the 3D space. Note that you may modify only the Origin and those direction vectors that are required for completely defining the space. When the X, Y, and Z direction vectors must be orthonormal, only the X and Y direction vectors must be entered. If these vectors are not orthonormal, OpenMaXwell will replace the X direction vector by a unit vector parallel to the original one. It then will replace the Y vector by a unit vector in the original XY plane, perpendicular to the X direction. Finally it will compute the Z direction vector as the vector product of the X and Y unit vectors.
Similarly, a plane is defined by an origin and two tangent vectors. Note that you may modify only the Origin and the X and Y direction vectors that are required for completely defining the plane.
An arrow has an origin and one tangential vector only. Note that you may modify only the Origin and the X direction vector that is required for defining the arrow or axis.
Finally, a point is defined by the origin vector only. Note that you may modify only the Origin because the direction vectors are nor required for defining a point.
The components of all vectors are defined in Cartesian components of a global coordinate system
Sometimes it is useful to rotate a given 3D space, plane, arrow or point around one of the axes of the global coordinate system. Sepcify the desired angle in degrees in the Angle box and press the corresponding X, Y, or Z button.
Press the Cancel button to close the dialog. Note that any modified data will not become effective.
Press the OK button to accept any modified data. Note that the dialog will close.
Responsible for this web page: Ch. Hafner, Computational Optics Group, IEF, ETH, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
Last update
17.02.2014