Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich
Switzerland, 2020-2021
| Andrey Ignatov | Luc Van Gool | Radu Timofte |
| andrey@vision.ee.ethz.ch | vangool@vision.ee.ethz.ch | timofter@vision.ee.ethz.ch |
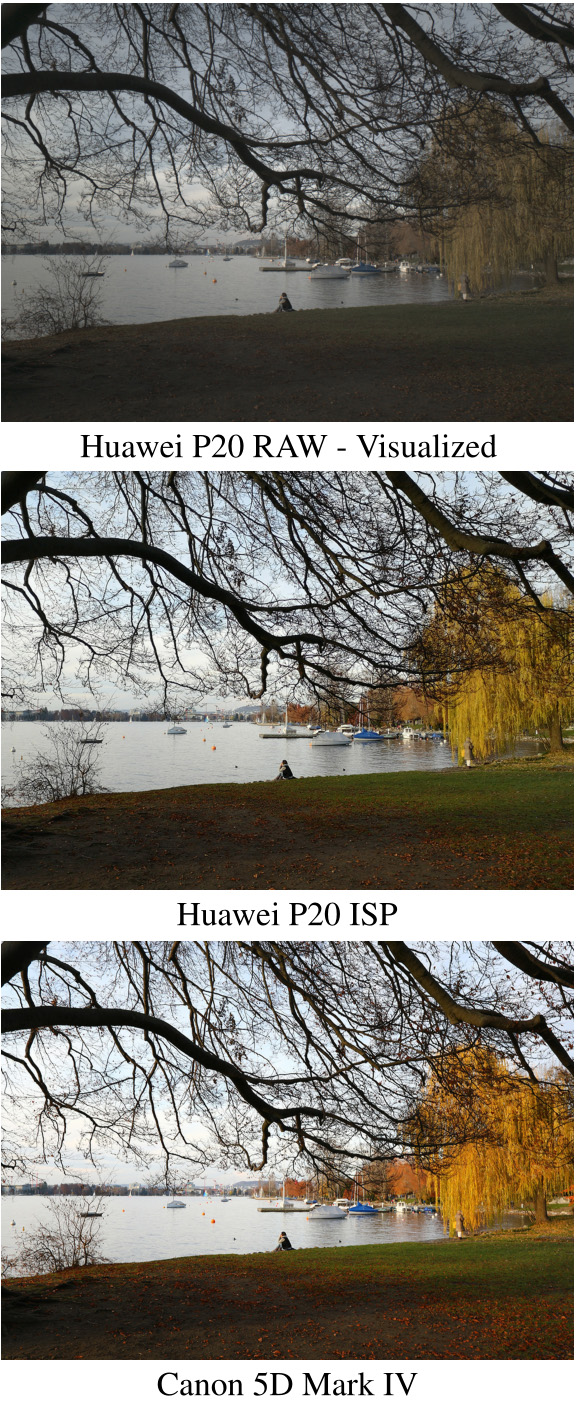
Abstract: As the popularity of mobile photography is growing constantly, lots of efforts are being invested now into building complex hand-crafted camera ISP solutions. In this work, we demonstrate that even the most sophisticated ISP pipelines can be replaced with a single end-to-end deep learning model trained without any prior knowledge about the sensor and optics used in a particular device. For this, we present PyNET, a novel pyramidal CNN architecture designed for fine-grained image restoration that implicitly learns to perform all ISP steps such as image demosaicing, denoising, white balancing, color and contrast correction, demoireing, etc. The model is trained to convert RAW Bayer data obtained directly from mobile camera sensor into photos captured with a professional high-end DSLR camera, making the solution independent of any particular mobile ISP implementation. To validate the proposed approach on the real data, we collected a large-scale dataset consisting of 10K full-resolution RAW-RGB image pairs captured in the wild with the Huawei P20 cameraphone (12.3 MP Sony Exmor IMX380 sensor) and Canon 5D Mark IV DSLR. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed solution can easily get to the level of the embedded P20's ISP pipeline that, unlike our approach, is combining the data from two (RGB + B/W) camera sensors. The dataset, pre-trained models and codes used in this paper are provided below.
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 Huawei-ISP
Huawei-ISP
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET
 RAW
RAW
 PyNET
PyNET

To get real data for RAW to RGB mapping problem, a large-scale dataset consisting of 20 thousand photos was collected using Huawei P20 smartphone capturing RAW photos (plus the resulting RGB images obtained with Huawei's built-in ISP), and a professional high-end Canon 5D Mark IV camera with Canon EF 24mm f/1.4L fast lens. RAW data was read from P20's 12.3 MP Sony Exmor IMX380 Bayer camera sensor - though this phone has a second 20 MP monochrome camera, it is only used by Huawei's internal ISP system, and the corresponding images cannot be retrieved with any public camera API. The photos were captured in automatic mode, and default settings were used throughout the whole collection procedure. The data was collected over several weeks in a variety of places and in various illumination and weather conditions.
Since the captured RAW-RGB image pairs are not perfectly aligned, they were first aligned globally using SIFT keypoints and RANSAC algorithm. Then, smaller patches of size 448×448 were extracted from the preliminary matched images using a non-overlapping sliding window. Two windows were moving in parallel along the two images from each RAW-RGB pair, and the position of the window on DSLR image was additionally adjusted with small shifts and rotations to maximize the cross-correlation between the observed patches. Patches with cross-correlation less than 0.9 were not included into the dataset to avoid large displacements. This procedure resulted in
It should be mentioned that all alignment operations were performed only on RGB DSLR images, therefore RAW photos from Huawei P20 remained unmodified, containing the same values as were obtained from the camera sensor.
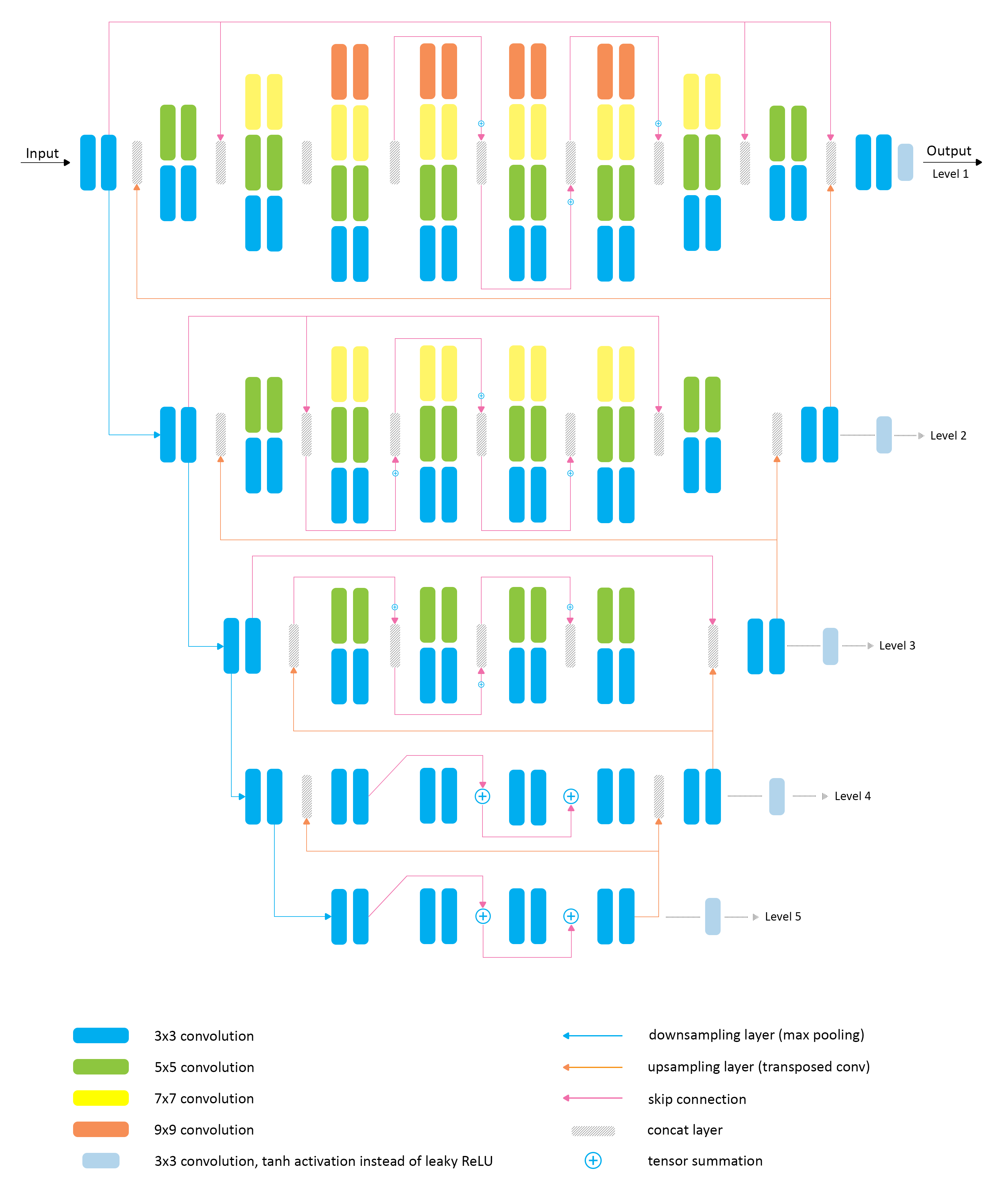
PyNET model has an inverted pyramidal shape and is processing the images at
The model
"Replacing Mobile Camera ISP with a Single Deep Learning Model",
Computer Vision Laboratory, ETH Zurich
Switzerland, 2020-2021